Temporary disability for a child. Getting a disability for a child. Causes of disability in children
How to register a disability - where to start: you need to know the procedure for registering a disability, what documents are needed to register a disability, what is the ITU commission for registering a disability
Cases when work capacity is limited due to an exacerbation of a disease or serious injury are a fairly common phenomenon in labor practice. In order to protect their rights and receive social support, an injured worker must go through a rather complex and lengthy procedure for registering disability. Where to start?
(click to open)
First, you need to carefully study the regulatory framework and determine the procedure for registering disability.
Secondly, you need to clearly understand what documents are needed to register a disability, where to get the work performance form for registering a disability, and decide on the functions and purpose of the ITU commission for registering a disability.
And thirdly, if necessary, distinguish between the features of registering a disability for a pensioner (bedridden), registering a disability for a child, how to register a visual disability, and how the procedure for registering a disability in oncology differs from others.
We will examine all these points in more detail in our article.

ITU commission for registration of disability
You can obtain the status of a disabled person on the basis of the Rules established by government decree number 95 in February 2006. Paragraph two of these Rules directly states that a citizen must first undergo a medical and social examination (MSE) - an MSE commission for registration of disability. Without the appropriate conclusion of medical specialists, you cannot count on state help.
Residents of Moscow, remembering the special federal status of their city, often do not know how to apply for disability in Moscow. Considering that the effect of the government decree of the Russian Federation is equivalent in all constituent entities of the Russian Federation, it should be noted that in the capital the procedure for registering disability occurs in strict accordance with the above document, as well as in other regions of Russia.
The basis for contacting a doctor is deterioration in health. A sick or injured person should visit his doctor, who will provide a referral to specialized specialists. They will record the results of the examination and examination in a separate report. Such a document has the right to be drawn up by both the attending physician and the group of doctors who observed the patient.
Particular attention is paid to the patient's condition. It is being determined whether he can live without outside help or continue working. In cases with children, their ability to learn, move independently and control their own behavior is determined.
Referrals for examination are given by the following government agencies:
- representatives of social protection authorities;
- branches of the Pension Fund (at the place of residence of the citizen affected by injury or illness);
- polyclinics (district or city).
If you became disabled due to the fault of a doctor, find out what punishment the doctor should bear for.
Features of the procedure
The legislation provides for both independent appeal of citizens to all necessary authorities, and through legal representatives who have all the powers to protect the interests of a sick person.
To obtain the status of a disabled person with the help of such a voluntary assistant, you must have the appropriate court decision in hand. It confirms the special condition of a person with disabilities and gives the representative the right to obtain a power of attorney at a notary’s office. can be found in this article.
To figure out how to register a disability, you must first clarify all the nuances of the procedure at the clinic or social service. Such consultation will help you avoid annoying mistakes.

Documents must be provided within ten days after submitting the application. This can also be done electronically. But the document must be certified by a qualified signature. After you have dealt with the paperwork, the immediate process of registering disability begins, which consists of 3 stages:
- Invitation to ITU. It may come in paper or electronic form.
- Conducting an ITU and obtaining a decision. No more than 30 calendar days pass from the date of filing the application until the examination. The decision is made immediately after the procedure. Explanations from medical experts can be provided immediately after the examination.
- Obtaining a certificate confirming the disability of a certain group.

Features of registration for certain groups of citizens
How to apply for disability for a child
To clarify how to register a disability for a child, you must also first consult with the social examination bureau or at the clinic.
In most cases, registering a disability for a child is no different from examining an adult. The documents are additionally accompanied by the passport of the adoptive parents, guardians or parents.
Another important nuance is the need to present the characteristics issued by the place of study (if the child is studying). For children with genetic or mental illnesses, permission from the attending physician will be required. This document will give teachers the right to disclose medical confidentiality in the characteristics compiled.
In general, there should be no problems with how to register a disability, since the procedure is approved by law with all the details for patients of any age.
How to apply for disability for a pensioner
Before applying for disability, a pensioner will have to do the following:
- Visit to a medical facility. The doctor performs an examination, after which he issues a medical report, which indicates the mandatory additional examination.
- if the doctor determines that the level of illness of the applicant corresponds to the definition of one of the disability groups, then the patient will be given a referral for a medical examination at the BMSE;
- Based on the results of a medical examination at the ITU, the applicant is issued a certificate - a certificate stating that he has been assigned a disability group;
- With the certificate, the pensioner goes to the Pension Fund office at the place of registration, where he receives the status of a disabled person. With this status, a citizen has the right to receive benefits and an increase in pension.
Sample performance characteristics for disability registration
Disabled people are one of the most vulnerable segments of the population. In this regard, the state assigns a disability pension.
Before applying for a disability pension, you need to collect all the necessary documents:
- certificate of passing the ITU;
- passport;
- SNILS card
Having a package of documents in hand, the citizen contacts the Pension Fund branch in his region and writes an application for payment of a disability pension.
Let's consider how much pension different groups of disabled people will receive.
- disabled people of the first group and disabled people from childhood of the second group – 8647.51 rubles per month;
- disabled people of the second group – 4323.74 rubles per month;
- disabled people of the third group - 3675.2 rubles per month;
- disabled children and disabled children of the first group - 10,376.86 rubles per month.

Subscribe to the latest news
Unfortunately, sometimes it happens that a baby is born with congenital health problems. In such situations, registration of disability for the child is required. But even if there are compelling reasons and clear rights to something in Russia, it is sometimes extremely difficult to formalize any legal authority. Because there are a lot of bureaucratic delays.
Procedure for establishing childhood disability
First, a medical certificate confirming the presence of a serious illness is required. This diagnosis must be made by a medical specialist. After which the pediatrician at the clinic at the place of residence refers to the medical examination (). This can also be done by a specialist who has identified the disease.
If for some reason a pediatrician or specialist does not give such a referral, you should ask for it. If the pediatrician or other doctor refuses this, you can contact the head physician (head) in writing with a request to oblige the pediatrician or other doctor to issue such a referral. A similar referral can also be obtained from the territorial social protection authorities.
Important! A child can also be granted a disability if there are mental disorders. In this case, a referral to medical examination can be issued by a mental health clinic or a psychiatrist.
Passing the ITU
 After receiving the required document, and even if it is missing, you should submit an application for passing the ITU to the examination bureau. The address of such an institution can be found at the clinic or at the social security agency.
After receiving the required document, and even if it is missing, you should submit an application for passing the ITU to the examination bureau. The address of such an institution can be found at the clinic or at the social security agency.
Advice! Even if there is no referral, you can independently initiate the procedure for conducting a medical and social examination.
During this procedure, you will receive a comprehensive medical examination. You will be given a list of doctors to avoid. As well as tests and additional examinations that need to be completed.
Most often, the medical commission includes the following specialists:
- ophthalmologist (ophthalmologist);
- surgeon;
- neuropathologist (neurologist);
- otolaryngologist (ENT);
- endocrinologist;
- orthopedist.
If children have other diseases in addition to the main illness, they may be sent for additional consultation to other highly specialized doctors (for example, a cardiologist, immunologist, geneticist, gastroenterologist, allergist, etc.).
Attention! In addition to a medical examination, children should definitely undergo general tests, and, if necessary, undergo other tests.
Do you need information on this issue? and our lawyers will contact you shortly.
Drawing up an inspection report
After passing the medical examination and receiving the conclusions of all the list of specialists and test results, you should contact the pediatrician in your area.
The pediatrician must draw up an epicrisis:
- with a brief description of the baby’s ontogenesis from the moment of his birth to the time of treatment,
- listing all the diseases he suffered,
- providing data on vaccinations performed.
If a child's disability is registered not with general therapeutic diseases, but with nervous, mental disorders, and intellectual disabilities, expert opinions and laboratory test results are provided not to the local pediatrician, but to a psychiatrist from a psychiatric dispensary.
Determination of disability
 When the act drawn up by the pediatrician or psychiatrist is ready, it is signed by the head physician of the clinic or dispensary. Only after this will it be possible to apply to the ITU to establish a disability for the child. And with the received comprehensive results and signatures of the head doctors, you will be redirected to the ITU.
When the act drawn up by the pediatrician or psychiatrist is ready, it is signed by the head physician of the clinic or dispensary. Only after this will it be possible to apply to the ITU to establish a disability for the child. And with the received comprehensive results and signatures of the head doctors, you will be redirected to the ITU.
With a package of received medical documentation, parents and their child must appear at the ITU meeting on the appointed date. If he cannot move independently and therefore is not able to come for an examination, it will take place at home or in a hospital ward.
To do this, one of the parents should contact the medical institution where the child is being treated for the appropriate certificate. Based on the results of the MSE, a definite answer will be given - whether the child is disabled or not.
In addition, they are also required to issue:
- a certificate of the established form confirming the fact of disability;
- extracts from the medical examination report.
Also, the MSE institution develops an individual program for the treatment and rehabilitation of a disabled child, and all other necessary certificates for the child’s disability. Since April 2018, the IRP of disabled children has been adjusted without changing the child’s social status and the need to re-apply to ITU institutions
If the answer is positive, then you must return to the clinic with the received expert opinion, certificates, and extracts. There the baby should:
- put on special account;
- prescribe the necessary treatment;
- provide a list of free medications and corresponding prescriptions.
Repeated procedures
 The legislation assumes that a person (regardless of age) can be cured of his existing chronic illness. The exception is only for some categories of disability group 1, where a person is recognized as disabled for life.
The legislation assumes that a person (regardless of age) can be cured of his existing chronic illness. The exception is only for some categories of disability group 1, where a person is recognized as disabled for life.
In other cases, an annual ITU is required, the results of which will be:
- disability is confirmed;
- an improvement in health status has been established, leading to the abolition of disability.
The repeated procedure is exactly the same as the initial one. After which the disability certificate is updated. Confirmation of disability is also sent to the clinic to continue receiving free medications.
Attention! In April 2018, the procedure for passing the ITU was significantly changed. In particular, the procedure for obtaining permanent disability, including for children, has been simplified. Now it can be established during the initial medical examination. Moreover, even carried out in absentia. In addition, the list of diseases for which disability can be assigned indefinitely has expanded.
Social assistance for disabled children
 After all the necessary formalities have been completed, you need to transfer information about disability to the Pension Fund, Social Insurance Fund and social security authorities. A child with a disability is entitled to a pension. The pension of disabled children in 2017 was 11,903.51 rubles.
After all the necessary formalities have been completed, you need to transfer information about disability to the Pension Fund, Social Insurance Fund and social security authorities. A child with a disability is entitled to a pension. The pension of disabled children in 2017 was 11,903.51 rubles.
Disabled people from childhood are paid:
- RUB 11,903.51 - with 1 category of disability;
- RUB 9,919.73 - for category 2;
- RUB 4,215.90 - for category 3.
Pension payments are established by Art. 18 Federal Law-166 of December 15, 2001 “On state pension provision in the Russian Federation.” They are indexed at least once a year (starting from April 1).
For disabled children and people with disabilities since childhood, the law also provides a special set of social services in kind. It includes three key areas and can be paid in a fixed monetary option.
Important! The recipient of a set of social services or his legal representatives may refuse to provide social services in kind in full or in parts, receiving in return material compensation as part of the EDV.
You can change the procedure for providing a set of services only from January 1 of each subsequent year, provided that the corresponding application to the Pension Fund is completed before October 1 of this year.
Download for viewing and printing:
Dear readers!
We describe typical ways to resolve legal issues, but each case is unique and requires individual legal assistance.
To quickly resolve your problem, we recommend contacting qualified lawyers of our site.
Last changes
In 2018, the list of diseases for which permanent or temporary disability for a long period (from 5 years) can be established was expanded. In particular, the following diseases can lead to permanent disability:
- chromosomal abnormalities (including Down syndrome),
- cirrhosis of the liver,
- deaf-blindness, deafness, blindness,
- phenylketonuria.
Disability is now established for 5 years not only for children with leukemia and malignant neoplasms, but also for other diseases, including malformations of the maxillofacial region, scoliosis, and autism.
At the first medical examination of children with thrombocytopenia and diabetes mellitus, disability is assigned until the child turns 14 years old.
There is a list of diseases for which MSE is carried out in absentia:
- diseases leading to high blood pressure, causing complications from the central nervous system;

Unfortunately, sometimes serious illnesses, injuries and accidents lead to disability. It's even more unfortunate that this is happening to our children. To an outsider, there is nothing sadder than a disabled child. And for parents of a sick baby, in addition to the usual worries and troubles, there are many other, specific ones. One of these moments is registration of disability.
What is disability, what does it give to a child and how to get it, read on.
Causes of disability in children
The concept of “disability” implies a person’s inability to carry out normal life in society, as we understand it, due to
- persistent violations of basic body functions. The main causes of disability are:
- congenital anomalies (heart defects, diseases of the respiratory system, musculoskeletal system and other vital organs);
- diseases of the nervous system (such as cerebral palsy), mental disorders;
- serious injuries of various origins.
What benefits does disability give to a child?
One of the reasons why it is necessary to register a child’s disability is the pension provided by the state. This is a cash benefit that is intended to purchase necessary medications and a variety of care products for a sick child.
In addition to the pension, a disabled child receives other benefits:
- the right to free travel in public transport (except taxis);
- preferential travel in railway, air and river transport;
- free spa treatment;
- free provision of necessary medical equipment (mobility aids, prosthetic and orthopedic products, etc.);
- free purchase of medications with a doctor’s prescription in case of outpatient treatment.
Privileges are granted not only to the disabled child himself, but also to his mother: this is a benefit when paying taxes on income, as well as the opportunity to work on a reduced work schedule, have additional leave and even retire early. These benefits depend on what disability group is assigned to the child, which, in turn, is determined by the medical commission. There are three disability groups for children, as well as for adults.
- Group I – the “heaviest” – is assigned to a child who is unable to take care of himself (move, eat, dress, etc.), cannot fully communicate with other children and needs constant supervision from adults.
- Disability group II implies certain restrictions in the actions listed above. Also, a disabled child of the second group is not capable of learning (and later of full-time work) or can only study in special institutions for children with specific disabilities.
- Group III is given to a child who can move independently, communicate, study, but is poorly oriented in unfamiliar situations, has a slow reaction and periodically needs control and care due to a special health condition.
Documents for registering disability for a child
As a rule, your local pediatrician helps you register your child’s disability. He must issue a referral to undergo a medical commission at your local clinic and to undergo all necessary tests.
The next stage is a medical and sanitary examination (MSE). To pass it you will need the following documents:

Within a certain time (usually it takes about a month), you will be given a certificate recognizing the child as disabled and assigning him a disability group. With this certificate, you should contact the Pension Fund office at your place of residence to apply for a disability pension.
In the clinic (or psychiatric dispensary) where the child is being observed, a doctor of the appropriate profile issues a referral for a medical and social examination (MSE).
A child with a hearing impairment is referred by an ENT (otolaryngologist), a child with a visual impairment is referred by an ophthalmologist, a child with a heart defect is referred by a cardiologist, a child with neurological developmental disorders is referred by a neurologist, and a child with a congenital genetic disorder is referred by a psychiatrist, and not a geneticist. Because children with genetic disorders, as a rule, have mild, moderate or profound mental retardation, which is diagnosed only by psychiatrists. It is mental retardation that interferes with the normal functioning of a child, and for this reason disability is assigned.
Check with your doctor in advance about the time frame within which you must visit all specialists and submit their reports to him.
Get expert opinions
When receiving a referral for medical examination from a specialist of the appropriate profile, be sure to clarify which doctors’ opinions you need to obtain and what tests you need to take.
As a rule, children are examined:
- otolaryngologist (ENT);
- ophthalmologist (ophthalmologist);
- surgeon;
- orthopedic surgeon;
- neurologist;
- endocrinologist
Please note that a surgeon and an orthopedic surgeon have different specializations: the latter deals with the treatment of the musculoskeletal system. Therefore, do not think that visiting one of the surgeons is enough.
In addition, you need to undergo general urine and blood tests.
If, in addition to the main disease, the child has concomitant diseases, additional opinions from relevant specialists will be required - for example, a cardiologist, urologist, speech therapist, geneticist, etc. Depending on the disease, other examinations may be required - for example, an ECG, audiogram, genetic blood test.
After all the doctors' opinions and tests have been collected, you must bring them to your local pediatrician, who will write a milestone epicrisis - a brief history of your child's development from birth to the present, which indicates all past diseases, diagnoses and vaccinations.
If your child’s diagnosis is not of a general therapeutic profile (say, heart disease, kidney disease, musculoskeletal system disease, poor vision or hearing), but, for example, autism, Down or Williams syndrome, schizophrenia, then you refer the doctors’ conclusions to a psychiatrist at the local psycho-neurological dispensary (PND).
Timing and priority
Next, the attending physician (or psychiatrist) must submit his conclusion to the head of the outpatient department (or the children's department of the PND) for signature. He may have to sign your documents from one to three weeks: the authorities have a lot to do, and besides, your baby is not the only one whose documents need to be studied and signed.
Expect that it may take more than 1-2 months to see specialists. For example, not every district children's clinic has a cardiologist, ophthalmologist, neurologist or orthopedic surgeon. Then you will have to take a referral and go to another clinic.
When you make an appointment with a specialist by phone, do not listen to the nurse on duty who will tell you: “The next appointment with an orthopedist is in a month.” You cannot wait a month - otherwise the deadlines will be missed! Just ask her to name the days and hours of the doctor's appointment and explain that you urgently need to see him as part of a disability assessment.
If in front of the door of each office they tell you: “There is a queue for appointments!” Calmly call the nurse and explain the situation: “We are registering a disability for the child. We need a specialist's opinion." In such cases, doctors and even people sitting in line to see a doctor most often cooperate. Firstly, if this is not the first time you are registering a disability for a child, and you already have a pink certificate in your hands, show it: a disabled child has the right to visit a doctor without an appointment and without a queue. And for those who have to apply for disability for the first time, it is worth remembering: if you wait for a month in line to see each specialist, you will not collect the necessary conclusions in six months! Your task is to collect documents quickly. Otherwise, for example, blood and urine tests may be overdue, and then what - start over?! And for a child, endless visits to doctors are tiring.
Don't forget your IPR certificates
Since you are being examined by all the specialists your child needs, immediately ask the doctor to write in his report recommendations for treatment and for the child to receive additional means of rehabilitation. These records will help you obtain additional procedures or benefits in the future. For example, an orthopedic surgeon may write that orthopedic shoes and insoles are vital for your child. An ENT specialist can issue a certificate for hearing aids.
Be sure to have all these certificates and expert opinions with you when you come to the commission at the ITU. If they are available, appropriate entries will be made in the individual rehabilitation program (IPR), on the basis of which orthopedic shoes or hearing aids will be issued by social security authorities free of charge.
Characteristics from school
If your child is a student, you must provide the attending physician (or psychiatrist), along with all reports from specialists, with a description from the school. It may be difficult to obtain it at school, especially if the school is special (for mentally retarded children). According to the law on secrecy of psychiatry, the school does not have the right to issue a reference for a child, simply because the mother asked. This requires a corresponding request. Therefore, when you come to a doctor (or psychiatrist) who is referring a child for medical examination, immediately, along with a list of specialists who need to be visited, ask them to write a corresponding request to receive a reference from the school. Otherwise, you will go to your doctor 10 times for each certificate!
And also keep in mind that the class teacher also has a lot of responsible things to do, methodological work and paperwork, so don’t expect that the teacher will drop everything and write a testimonial in a day, and even sign it with the director and put two necessary stamps on the document (round and square). This will take at least a week.
Registration for the ITU commission
To pass the ITU, you must sign up for the commission in advance. To do this, you need to personally come to the ITU office, having previously called there and found out the days and hours of reception.
If this is not the first time you are registering a disability for your child, sign up for ITU without waiting for the end of the disability period. The next re-examination can be completed 1–2 months before the end of the previous period.
You can sign up for a commission when you start visiting all the specialist doctors. By the time you visit them and you have collected all the necessary documents, your turn will be approaching.
Documents for registration on the ITU commission
In order to sign up for a commission at the Bureau of Medical and Social Expertise (MSE), you will need to submit the following documents:
- completed form No. 080/u-06 (that is, the conclusion of the chief physician of a children's clinic or children's department of acute care);
- outpatient card from the clinic;
- characteristics of a child from school;
- a pink certificate from the previous commission for determining disability (if disability is not registered for the first time);
- child’s passport with registration;
- for children under 14 years of age - the child’s birth certificate and a certificate of permanent (form 9) or temporary registration;
- passport of one of the parents or guardian of the child who accompanies him to the ITU;
- application from the parent or guardian of the child to assign the child the status of a disabled child (filled out directly at the ITU office).
Change of ITU date
If for a valid reason you need to reschedule the ITU date, please contact the bureau in advance with such a request.
If the child’s condition is such that he does not walk or cannot be taken to the ITU office for a commission, then a medical and social examination can take place at home. You will need to obtain an appropriate conclusion about passing the ITU commission at home from the clinic or hospital where your child is being treated.
Don't be late!
When you go to the ITU commission, be sure to take with you a change of shoes for you and your child, as well as a clean diaper for the examination.
Come to the commission on the specified date and exactly at the appointed time. Don't be late! If you mix up the date, time, or are simply late, you may not be accepted, and then you will have to sign up for the commission and wait for your turn again. The queue lasts about a month. During this time, test results and even doctors’ opinions may become outdated. And the attending physician who writes the conclusion always states: the more recent the conclusions of all medical specialists, the better for the ITU.
Deadline for establishing disability
Of course, after reading all this, it will seem to you that there is a long and difficult road ahead. But it will be difficult only the first time. When you re-register for disability, you will already know how to act more rationally and overcome bureaucratic obstacles. Moreover, not every child needs to undergo disability recertification every year. In some cases, the child's condition is monitored by the ITU once every two years, since the health condition may remain stable, worsen or improve. And sometimes, say, in the case of congenital genetic diseases (for example, Down or Williams syndrome), the child is observed for no more than 4 years, after which disability is established until the age of 18. Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation No. 95 “On the procedure and conditions for recognizing a person as disabled” contains a list of diseases for which disability is established until the child reaches 18 years of age or for life.
Unfortunately, children are not immune from external influences, and therefore there are cases when various diseases take their toll on them and there is a need to register for disability.
On the territory of the Russian Federation, the legislative framework for the issue of the procedure and regulation of disability for adults and children is the same.
As for the order of registration, there are slight differences in this regard. Let's look at everything in more detail.
Who belongs to the group of disabled children? Legislative framework of the issue
Children's disabilities are clearly regulated by the legal framework, which provides for registration procedures, social benefits and rights to rehabilitation.
In particular, we are talking about such laws, How:

It is worth noting that any child who has any disease (cerebral palsy, autism and others) due to which he cannot live a normal life, is limited in movement, and so on has the right to receive disability.
There is a certain procedure for obtaining disability.
General procedure for registering disabled status for a child
The big picture registration of disability for a child it looks like this:

Collection of necessary documentation
The documentation required to conduct a medical examination is clearly regulated by the Ministry of Labor. It includes:

As for the birth certificate or passport, there must be a copy.
To carry out the examination, foreigners, in addition to these documents, must present a document confirming their status on the territory of the Russian Federation (we are talking about a certificate of a forced migrant, a residence permit, a temporary residence permit, and so on).
The ITU Commission does not have the right to demand any additional documents from parents, since this list is exhaustive and is clearly regulated by current legislation.
Parents have the right to provide a package of documents both in person and electronically. When sending documents via e-mail, an electronic stamp must be affixed. But as practice shows, the best option is personal transfer of documents (otherwise there is a possibility of losing documents).
Where to contact
As a rule, the initiator of the referral to the commission is the attending physician himself, but there are cases when parents decide this issue themselves.
 In the event that a child’s illness is a reason for registering disability, you must first contact the local pediatrician assigned to the child.
In the event that a child’s illness is a reason for registering disability, you must first contact the local pediatrician assigned to the child.
It is he who will be able to advise parents and act as an initiator. However, if the child is registered in any department, then you should initially contact them about this.
For example, a child is registered with a surgeon, therefore, it is necessary to contact him first. He will write out the directions and tell you about further actions.
It is worth noting that disability is assigned only in extreme cases when medicine is powerless. Unfortunately, recently, parents have been trying to apply for disability even for minor illnesses that can be cured within a month. If you contact the commission with such a disease, disability will be denied immediately.
Features of design with various diseases
The beginning of the disability registration procedure depends on the presence of a certain disease (more precisely, different attending physicians issue a referral). Let's take a closer look.
Diseases of the musculoskeletal system
 If there is a disease with the musculoskeletal system, issuing a referral falls on the attending surgeon, who determines the order of further actions.
If there is a disease with the musculoskeletal system, issuing a referral falls on the attending surgeon, who determines the order of further actions.
In most cases, disability can be assigned for a period of 1 year with further confirmation.
With Shereshevsky-Turner syndrome
Today, there is a lot of controversy surrounding disability with this disease. In most cases, when a child with such a disease is assigned disabled status, it is removed after a year.
However, disability can only be established if:
- the child has problems with the development of internal organs;
- there are serious disruptions of the endocrine system;
- there is a failure in mental development.
If the above conditions are not met, disability will be denied.
By vision
If you have vision problems, when trying to apply for disability, the first thing you should do is contact an ophthalmologist who is directly involved in treatment.
As a rule, diseases from this group lead to lifelong disability.
Autism
In most cases, a psychologist recommends assigning a disability. In no case does this mean that the child is now not like everyone else. Many experts in this field recommend carrying out MSEC with only one goal - a significant reduction in expenses for rehabilitation, the possibility of treatment in the best clinics of the Russian Federation for free, which entails a rapid improvement in the child’s health.
In case of autism, disability is assigned for one year, and subsequently extended if necessary. 
Asthma
Disability in this case is possible only with a chronic disease, which entails constant attacks of suffocation. Despite the fact that with such a disease the likelihood of becoming disabled is quite small, it is still possible.
However, you must be prepared for the fact that every year you must make every effort to prove the presence of this disease.
ZPR
 If you have this disease, you should contact your treating psychotherapist for a consultation.
If you have this disease, you should contact your treating psychotherapist for a consultation.
If it is possible to obtain disability, he will determine the next steps for the child’s parents. But as practice shows, the likelihood of receiving disabled status is low.
cerebral palsy
If you have cerebral palsy, you must first contact your treating neurologist for a referral, and then your local pediatrician.
In this case, disability is issued for a period of 1 year, then a recommission is required.
Design features in different regions
In all regions of our country, the procedure for registering disability for a child is the same. There is a small nuance to this.
The fact is that if a child who is referred to MSEC is a student at a school or kindergarten, a reference from this institution is required. If the parents moved to another city, they must personally or through a request request that a reference be sent. Otherwise, the commission may simply not accept the child and the procedure will be scheduled for the next year.
If the characteristics are required in the form of a request, it is submitted directly by the attending physician.
The procedure for registering a disability for a child is outlined in the following video:
 The story of the pilots who bombed Hiroshima and Nagasaki
The story of the pilots who bombed Hiroshima and Nagasaki Smooth capacity charging: what to choose?
Smooth capacity charging: what to choose?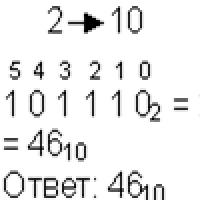 Small Faculty of Mathematics
Small Faculty of Mathematics “Why do you dream about a round dance in a dream?
“Why do you dream about a round dance in a dream? Why do you dream about the church inside: interpretation of the meaning of the dream according to various dream books for men and women
Why do you dream about the church inside: interpretation of the meaning of the dream according to various dream books for men and women Dream interpretation of persimmon, why do you dream of persimmon in a dream to see Persimmon in a dream why
Dream interpretation of persimmon, why do you dream of persimmon in a dream to see Persimmon in a dream why Enchanted soul Meaning of karmic numbers
Enchanted soul Meaning of karmic numbers